If your child has a congenital heart defect, it means that your baby was born with a problem with the structure of his heart.
Some congenital heart defects in children are simple and do not require treatment. Other congenital heart defects in children are more complex and require multiple surgeries over many years.
Knowing about your child's congenital heart defect can help you understand the situation and what to expect in the months and years to come.
Types of congenital heart disease
There are many types of congenital heart disease, and sometimes they are combined. Some common mistakes:
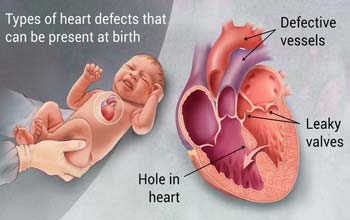
Septal defects - there is a hole between the two chambers of the heart (commonly called a "hole in the heart")
Correction of the aorta: Here the main large artery in the body called the aorta is narrower than usual.
Pulmonary valve stenosis: where the pulmonary valve that controls blood flow from the lower right chamber of the heart to the lungs is narrower than normal.
Great Artery Transplantation - Where the pulmonary and aortic valves are swapped and the locations where the arteries to which they are connected are swapped.
Undeveloped heart - A part of the heart that is not developing properly, making it difficult for the body or lungs to pump enough blood.
Causes
Doctors never know why a baby has a congenital heart defect. They walk in families.
Things that make them more:
Problems with genes or chromosomes in children such as Down syndrome
Taking certain medications or alcohol or drugs during pregnancy
Viral infection of the mother with rubella (German measles) during the first trimester of pregnancy
Signs & Symptoms
In some cases, symptoms of congenital heart disease do not appear until after birth. Newborns with heart defects may experience:
Blue lips, skin, fingers, and toes
Shortness of breath or trouble breathing
Difficulties in eating
Low birth weight
Chest pain
Growth retardation
In other cases, symptoms of a congenital heart defect do not appear until many years after birth. As symptoms develop, they can include:.
Abnormal heart rhythms
Dizziness
Difficulty breathing
Epilepsy
Inflammation
Fatigue
Diagnosis
In some cases, fetal ultrasound can detect congenital heart defects before the baby is born.
Some types of congenital heart defects develop immediately after birth. Less serious defects do not appear until the child is of legal age. Some congenital heart defects are diagnosed after hearing a heart murmur.
Depending on the child's symptoms or a heart murmur, the doctor may order one or more of the following tests to diagnose a congenital heart defect:
Electrocardiogram
Echocardiogram (a cardiac ultrasound)
Chest x-ray
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT)
Cardiac catheterization
Blood test for genetic analysis.
If your child is diagnosed with a chromosome or other genetic abnormality, genetic counseling can help you identify the risk of heart defects in other children that she may have in the future.
Treatment
Children with mild heart defects do not need treatment. But some babies have severe symptoms that require medical or surgical treatment during the first year of life. They take care of:
Pediatric Cardiologists - Specialists in treating pediatric heart problems.
OR
Pediatric cardiac surgeons: specialists in pediatric cardiac surgery
Procedures performed by cardiac catheterization, such as balloon angioplasty or valvuloplasty, dilate blocked blood vessels or valves. Another method, the transcatheter device housing, can close abnormal openings or holes in the heart or blood vessels without surgery.
Some problems, such as small or medium-sized ventricular septal defects, may close or become smaller as the child grows. While you wait for the hole to close, your child will need to take medicine.
Complex defects initially detected may require a series of operations completed before the age of 3 in the child.
Comments
Post a Comment